In the modern digital age, CDN servers are crucial technology that enhances the loading speed of content on websites. So, how can you set up CDN servers? Let's explore how to configure them to optimize your website.
Understanding CDN
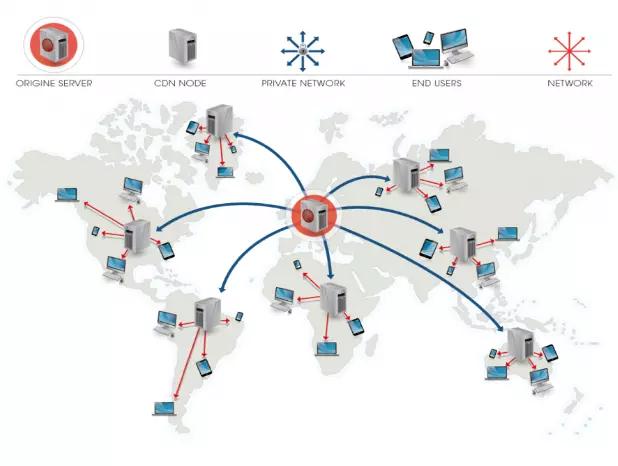
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a content distribution system designed to enhance the performance and loading speed of content on the internet. The way CDN servers work is by storing content on a global network of distributed servers at various locations worldwide. When users access a website or request content, the CDN server will automatically select the nearest physical server to serve the content, reducing latency and optimizing the user experience. This helps reduce the load on the origin server, protect the website from DDoS attacks, and optimize page loading speed.
CDN servers work by optimizing the distribution of content on the internet. Here's the basic operation of a CDN system:
Content Copy: Initially, website content or online services are copied and stored on multiple distributed CDN servers located at different geographical points worldwide.
Select the Nearest Server: When users access the website or request content, the CDN system will automatically determine the nearest CDN server based on the user's physical location.
Serve Content from the Nearest Server: The nearest CDN server will serve content to the user, reducing latency and optimizing website or online content loading speed.
Caching: CDN servers also use caching to store a copy of content on servers close to users. This helps reduce the load on the origin server and improve performance.
Content Optimization: In addition to content storage, CDN servers can optimize it by compressing images, combining document files, and even providing security against online attacks.
Protection Against Attacks: The CDN system can help protect websites or online services from network attacks like DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) by distributing traffic across multiple servers and filtering unwanted traffic.
CDN servers help users improve loading speed, reduce latency, and optimize the user experience when accessing websites or online services, especially for users far from the origin server.
How to Set Up CDN Servers
To set up CDN servers, you need to follow these basic steps:
Choose a Provider: Begin by selecting a CDN provider that suits your needs. There are numerous options available for individuals or businesses, including Cloudflare, Akamai, Amazon CloudFront, and many others. This choice depends on your technical requirements, budget, and geographic location.
Register an Account: Sign up for an account on the chosen CDN provider's website that you consider appropriate and manageable for you.
Add Your Website: Once you have an account, add your website or application to the CDN system by providing your domain name.
Configure Your Website: You'll need to configure your website on the CDN provider's dashboard. This includes settings such as cache management, image optimization, and security configurations.
Change DNS: Usually, you'll need to change DNS settings to direct your domain to the CDN server. The CDN provider will provide detailed information on how to do this.
Check and Optimize: After changing DNS, check and ensure that your website is using CDN correctly. Monitor performance and optimize CDN settings to ensure your website operates efficiently.
Security and Protection: Make sure you have configured your CDN appropriately to provide security for your website, including protection against DDoS attacks and other security issues.
Regular Monitoring and Adjustments: Regularly monitor and adjust CDN settings based on data and changing needs for your website.
Please note that specific steps may vary depending on the specific CDN provider and your deployment model. Always refer to documentation and support from your CDN provider to ensure effective CDN setup and management.
Benefits of Setting Up CDN Servers
Setting up CDN servers offers numerous benefits for your website or application, including:
Improved Page Loading Speed: CDN servers reduce latency and optimize the loading speed of web pages, providing a faster and more comfortable user experience.
Reduced Load on the Origin Server: By distributing the load among multiple globally distributed CDN servers, your origin server's load is significantly reduced, ensuring efficient platform operation.
Bandwidth Savings: CDN servers save internet bandwidth by serving content from the nearest servers to users, reducing network bandwidth costs.
Security and Protection: CDN systems often come with robust security features to protect your website from network attacks, such as DDoS attacks, SQL injection, and Cross-Site Scripting (XSS).
Optimized Images and Content: CDN servers have the ability to optimize images and document files to reduce size and improve website performance.
Global Distribution: CDN servers place servers at various geographical locations worldwide, serving content to a global audience.
Mobile Experience Optimization: CDN servers optimize the mobile experience by providing backup content for mobile devices.
Statistics and Monitoring: You can monitor and track your website's performance through the statistics and monitoring tools provided by CDN servers.
Scalability: CDN servers allow you to easily scale resources and optimize your website to cope with increased user traffic.
In conclusion, in the rapidly evolving online world, using CDN servers is not just an option but a necessity. CDN servers improve performance, security, and optimization of your website or application, providing a better user experience and reducing operational costs. Remember that CDN servers not only improve performance but also provide security, save bandwidth, and offer scalability. With the ever-growing internet, CDN servers are an essential tool to ensure you stay ahead in the online performance race.