I. Client and server
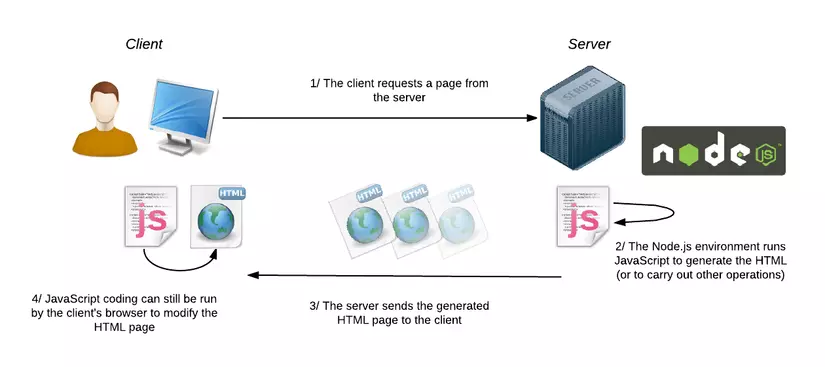
- Clients and servers communicate by exchanging messages request and response.
- Each computer is identified by IP address
- To communicate, server/client needs to connect to IP address of each other to open the socket between 2 computers.
II. Create a server using http module
1. http module
- http is a built-in module of Node.js, used to create HTTP server which listens to server ports and give a response to the client.
- http stands for Hyper Text Transfer Protocol.
// require http module
const http = require('http'); // create HTTP server using createServer()
// whenever user sends a request to the server, callback fnc will be fired.
http.createServer((req, res) => { // send a response to client res.write("Welcome!"); // end the response res.end();
}).listen(3000); // server is listening on port 3000 // or http.listen(3000);
- http.listen(port, hostname - IP address, backlog - max length of pending connections' queue, cbFnc - fired when listener has been added): makes server listen to a specific port on computer.
- http.get(): sets method to GET, returns an object containing user's request.
- http.request(): returns an object containing user's request.
2. HTTP header
- HTTP header allows client and server pass additional information with an HTTP request or response.
- Request headers contain infomation about the resource to be fetched.
- Response headers provide information about response's location or the server itself.
- Representation headers is information about the body of the resource.
- Payload headers is information about payload data such as content length, transport's encoding.
// writeHead(statusCode - number,[statusMsg - string],[headers - object]
// a response header sending text
res.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'text/plain'});
// a response header sending html
res.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'text/html'});
III. Serve data to client
1. Buffers and streams: consuming data before it all arrived
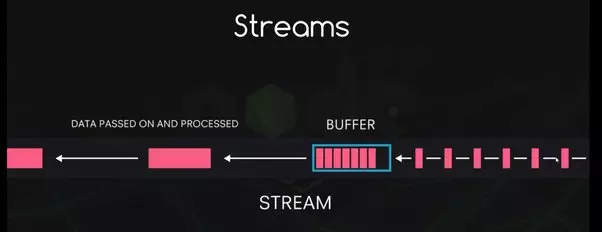
- Buffers is a temporary storage that a stream takes to hold data until it is consumed.
- Streams transfer data with a better performance.
- There are 4 types of streams:
Readable streams to read data from a stream.
const fs = require('fs');
// create read stream, read file and return chunck of data little by little
let myReadStream = fs.createReadStream('filename', 'utf8');
// createReadStream inherits EventEmitter so it can listen to events -> cbFnc is executed when a chunk arrives
myReadStream.on('data', (chunck/buffer) => { // do smt with a chunk of data
});
Writable streams to write data to a stream.
let myWriteStream = fs.createWriteStream('filename');
myWriteStream.write('data');
Duplex can read and write to a stream.
Transform streams can read and write to a stream but data can be modified while reading/writing.
2. Pipes
- Takes data from read stream then pipes them to write stream
const fs = require('fs');
// Step 1: Create read stream
let myReadStream = fs.createReadStream('original.txt','utf8');
// Step 2: Create write stream
let myWriteStream = fs.createWriteStream('copy.txt'); // Step 3. Use pipe() myReadStream.pipe(myWriteStream);
3. Serve HTML page
http.createServer((req, res) => {
res.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'text/html'})
let myReadStream = fs.createReadStream("index.html", 'utf8');
// res object is a writable stream
myReadStream.pipe(res);
// or
fs.createReadStream("index.html", 'utf8').pipe(res);
});
4. Serve JSON data
const person = { "name": "Vivian", "gender": "female"}; http.createServer((req, res) => {
res.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'application/json'})
let data = JSON.stringify(person);
res.end(data); // arg should be string or buffer
});
IV. Express JS
- An easy and flexible routing system.
- Integrating with many templating engines to build dynamic content.
- Containing middle ware framework
- Installation:
npm install express --save
// return a function
let express = require('express');
let app = express(); // app.get(route, cbFnc) instructs what to do when a get request to the / route is called
app.get('/', (req,res) => { // send input to the client res.send("Hello world!");
}); app.listen(3000);
- app.set(name,value): assigns the setting name to value, configure the behavior of the server.
- res.send(data - string or buffer or object) : sends the HTTP response
- res.sendFile(path, [options], [cbFnc]): transfers the given file and sets Content-Type value based on the given file extention.
- res.render(view,[{}],[cbFnc]): render a view (template for dynamic content) and sends rendered HTML string to client. {} contains embedded data to be passed to view (.ejs).
1. HTTP methods - kinds of request client make
- GET
- POST
- DELETE
- PUT
2. Route paramters - dynamic request
// param can be named anything
app.get('/profile/:paramName', (req,res) => { // param is accessed through req object req.params.paramName; });
3. Query strings
- Additional data added to a HTTP request in form of name-value pair
- Separated by & if there are many query strings:
?person=vivi&dept=it - Access query string:
req.query-> return an object{dept: 'it', person: 'vivi'}
V. Templating (EJS)
- Used to embedded dynamic data to HTML.
- Installation:
npm install ejs --save
1. Templating syntax
- Output data:
<%= %> - Output JS code:
<% %> - Looping
<% data.arrayName.forEach((item) => {%>
<li><%=item%></li>
<%});%>