Date and ISODate in MongoDB
 In MongoDB, ISODate is used to store date objects in ISO 8601 format, which is a standard for date and time representation. The ISODate is often used for handling date fields within MongoDB documents.
In MongoDB, ISODate is used to store date objects in ISO 8601 format, which is a standard for date and time representation. The ISODate is often used for handling date fields within MongoDB documents.
Syntax
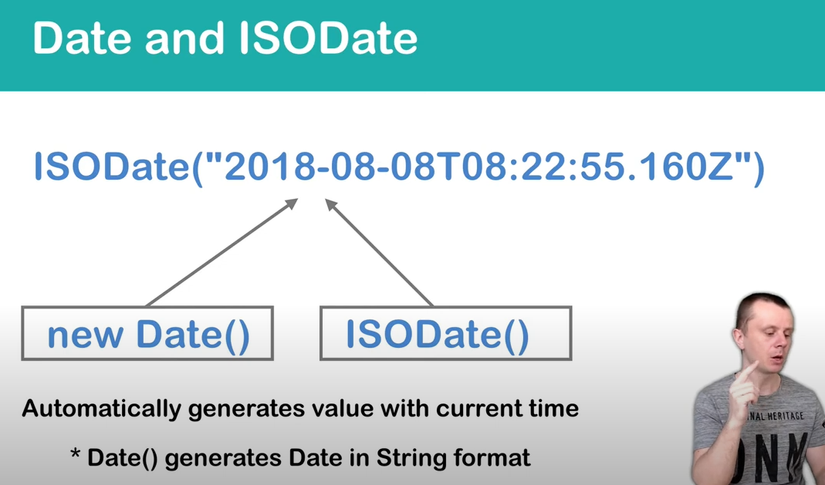
You can specify either of the following formats: Date() returns the current date as a string in mongosh. new Date() returns the current date as a Date object. mongosh wraps the Date object with the ISODate helper. The ISODate is in UTC. You can specify a particular date by passing an ISO-8601 date string with a year within the inclusive range 0 through 9999 to the new Date() constructor or the ISODate() function. These functions accept the following formats:
- new Date("<YYYY-mm-dd>") returns the ISODate with the specified date.
- new Date("YYYY-mm-ddTHH:MM:ss") specifies the datetime in the client's local timezone and returns the ISODate with the specified datetime in UTC.
- new Date("YYYY-mm-ddTHH:MM:ssZ") specifies the datetime in UTC and returns the ISODate with the specified datetime in UTC.
- new Date(<integer>) specifies the datetime as milliseconds since the UNIX epoch (Jan 1, 1970), and returns the resulting ISODate instance.
Behavior
Internally, Date objects are stored as a signed 64-bit integer representing the number of milliseconds since the Unix epoch (Jan 1, 1970).
Not all database operations and drivers support the full 64-bit range. You may safely work with dates with years within the inclusive range 0 through 9999.
Examples
Use Date in a Query If no document with _id equal to 1 exists in the products collection, the following operation inserts a document with the field dateAdded set to the current date:
db.products.updateOne( { _id: 1 }, { $set: { item: "apple" }, $setOnInsert: { dateAdded: new Date() } }, { upsert: true }
)
Return Date as Date Object