Lời mở đầu
Chào các bạn, hôm nay tôi xin giới thiệu với các bạn về 1 framework API mà tôi mới vọc vạch mấy tuần trước. Tại sao tôi lại giới thiệu framework này, âu cũng là do cái slogan của team này bắt mắt quá  .
.

FastAPI framework, high performance, easy to learn, fast to code, ready for production
Vậy fastAPI là gì, mời các bạn đọc phần tiếp theo.
Khái niệm
FastApi là 1 web framework dùng để build API có hiệu năng cao, code dễ ẹc, đơn giản nhưng cũng hỗ trợ tốt cho việc làm sản phẩm.
Đặc điểm:
- Fast: Hiệu suất cao ngang với NodeJS và Go.
- Fast to code: Code nhanh hơn, tốc độ code các features tăng khoảng 200 đến 300 %.
- Fewer bugs: do đơn giản nên giảm số bugs của developper đến 40%.
- Intuitive: hỗ trợ code dễ hơn với tự động gợi ý, debug cần ít thời gian hơn so với trước.
- Easy: được thiết kế sao cho dễ dùng dễ học.
- Short: Tối thiểu việc lặp code. Các tham số truyền vào có nhiều tính năng. Ít bugs.
- Robust: hiệu năng mạnh mẽ, có thể tương tác API qua docs.
Cài đặt
Yêu cầu: Python 3.6+.
FastAPI được build dựa trên OpenAPI (trước có tên Swagger), phần web được support bởi Starlette, còn phần data được support bởi Pydantic.
FastAPI CLI
Để cài đặt framework này trên Ubuntu, bạn cần phiên bản python 3.6.
pip install fastapi
Bạn cũng cần ASGI server khi deploy sản phẩm như Uvicorn hoặc Hypercorn.
pip install uvicorn
Nói sơ qua về ASGI 1 chút, ASGI kế thừa từ WSGI. Mà WSGI là 1 chuẩn giao tiếp giữa web server và Python application server. Trước thì có mod_python của Apache nhưng do không phát triển và không an toàn nên WSGI sinh ra. WSGI có những tác dụng như sau:
- WSGI mang tính linh hoạt: dev có thể chuyển đổi thành phần web như chuyển từ Gunicorn sang uWSGI.
- WSGI xử lý nhiều request cùng lúc thay webserver và quyết định request nào được chuyển tới application web. Hình minh họa chôm được ở trang (fullstackpython.com):
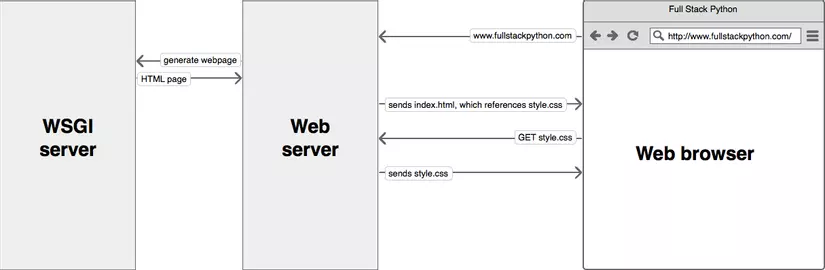
Nếu như WSGI là tiêu chuẩn cho các synchronous Python appsthì ASGI là tiêu chuẩn cho cả synchronous và asynchronous Python apps. ASGI phù hợp với tất cả ứng dụng sử dụng WSGI do có cơ chế tương thích ngược.
Ok dông dài đủ rồi, chúng ta tiếp tục tìm hiểu xem FastAPI còn cung cấp những tiện ích gì nhé.
FastAPI Docs
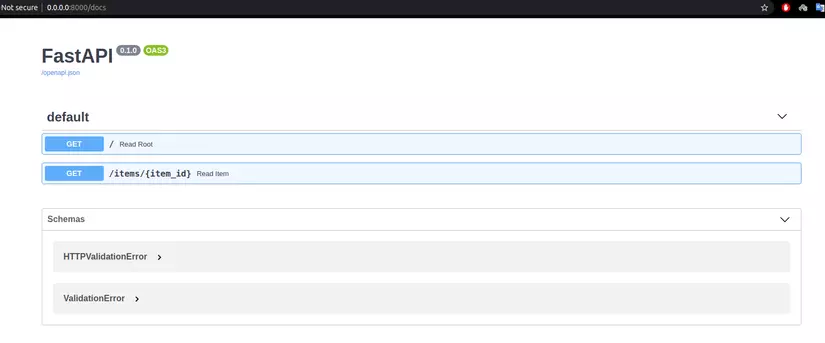
Do based trên OpenAI mà trước đó có tên là Swagger nên FastAPI cung cấp doc có giao diện dễ nhìn, dễ sử dụng. Ví dụ minh họa:
Khi bật doc bằng local url http://0.0.0.0:8000/docs.
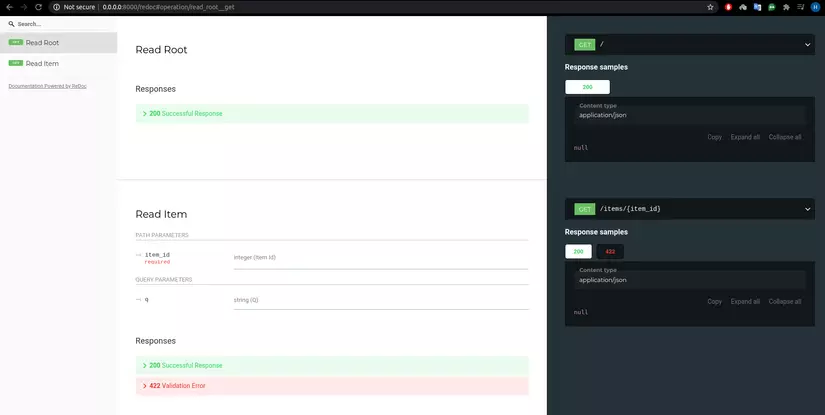
1 giao diện khác của FastAPI docs http://0.0.0.0:8000/redoc.
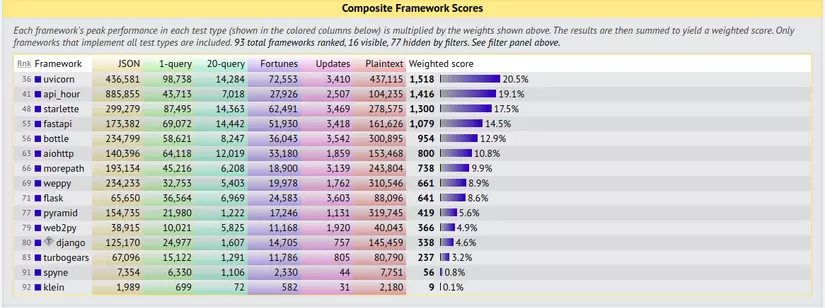
Performance
Các bạn có thể test hiệu năng của các web framework trên trang này (https://www.techempower.com/benchmarks/)
Optional Depencies
Do FastAPI based trên Pydantic và Starlette nên có hỗ trợ thêm 1 số thư viện có cũng được không có cũng không sao:
Pydantic:
ujson: JSON "parsing" nhanh hơn.email_validator: validate email.
Starlette:
requests: khi bạn muốn tạo request, dùngTestClient.aiofiles: khi bạn muốn dùngFileResponsehoặcStaticFile.jinja2: nếu bạn muốn dùng các mẫu config mặc định.python-multipart: hỗ trợ "parsing" với request.form().itsdangerous: hỗ trợSessionMiddleware.graphene: hỗ trợGraphQL.
FastAPI:
uvicorn: ASGI server phục vụ cho ứng dụng của bạn.orjson: nếu muốn dùngORJSONResponse.
Nếu muốn dùng hết thư viện trên thì bạn chỉ cần dùng 1 câu lệnh đơn giản.
pip install fastapi[all]
Hướng dẫn cơ bản
Create a simple API
Về cơ bản thì code dễ như ăn kẹo, bạn tạo 1 file main.py.
from fastapi import FastAPI #import class FastAPI() từ thư viện fastapi app = FastAPI() # gọi constructor và gán vào biến app @app.get("/") # giống flask, khai báo phương thức get và url
async def root(): # do dùng ASGI nên ở đây thêm async, nếu bên thứ 3 không hỗ trợ thì bỏ async đi return {"message": "Hello World"}
Sau đó chạy dòng code này để chạy app
uvicorn main:app --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8000
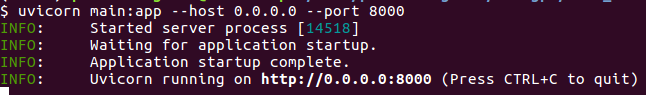
P/S: nếu bạn làm trong môi trường phát triển có thể thêm --reload để tự động restart sau khi thay đổi code.
Tiếp sau đó vào xem thử thành quả phát http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs.
Ấn vào Try it out -> Execute -> API trả về response.
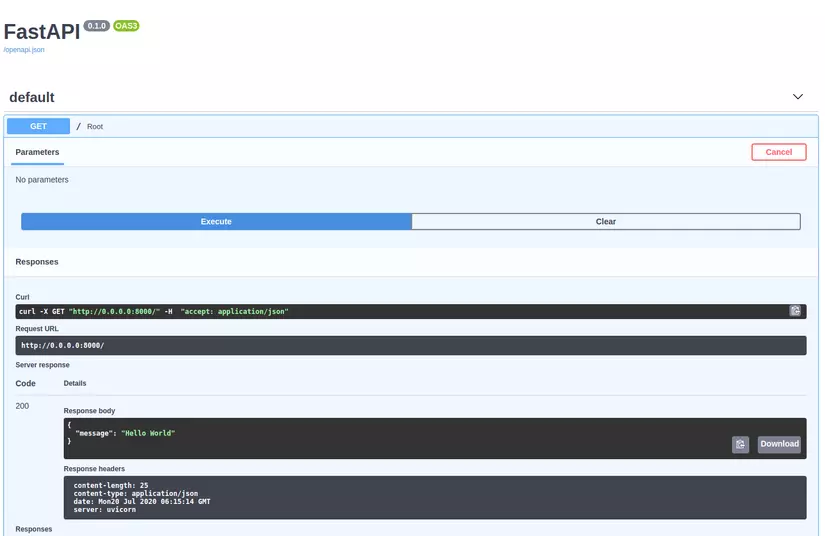
Giao diện API này được thiết kế dựa trên OpenAPI. Bên đó có hẳn 1 khái niệm để define API gọi là "Schema". Nếu bạn tò mò thì vào link này http://127.0.0.1:8000/openapi.json.
{ "openapi": "3.0.2", "info": { "title": "FastAPI", "version": "0.1.0" }, "paths": { "/": { "get": { "summary": "Root", "operationId": "root__get", "responses": { "200": { "description": "Successful Response", "content": { "application/json": { "schema": {} } } } } } } }
}
Nói chung bạn chỉ cần 6 bước để tạo 1 API
- Bước 1: import fastapi
- Bước 2: tạo 1 instance của class FastAPI
- Bước 3: tạo đường dẫn, bắt đầu từ
/ - Bước 4: khai báo phương thức HTTP: post, get, put, delete hay options, head, patch, trace
- Bước 5: khai báo hàm
- Bước 6: trả về content với format dict, list, str, int, ...
Path Parameters
Bạn có thể truyền param thông qua đường dẫn.
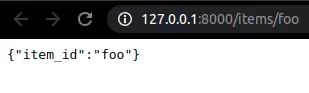
from fastapi import FastAPI app = FastAPI() @app.get("/items/{item_id}")
async def read_item(item_id): return {"item_id": item_id}
Biến item_id trên đường dẫn sẽ truyền vào hàm read_item với thông qua param trùng tên item_id. Test thử http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/foo.
Path parameters with types
Bạn cũng có thể khai báo định dạng của param để trả về khi truyền biến đúng định dạng sẽ trả về giá trị.
from fastapi import FastAPI app = FastAPI() @app.get("/items/{item_id}")
async def read_item(item_id: int): return {"item_id": item_id}
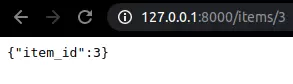
Data validation
Còn nếu không đúng định dạng thì trả về thông báo. Mọi dữ liệu được validate đều dựa trên Pydantic.

Order
Nếu bạn có khai báo đường dẫn trùng lặp như thế này:
from fastapi import FastAPI app = FastAPI() @app.get("/users/me") # <- here
async def read_user_me(): return {"user_id": "the current user"} @app.get("/users/{user_id}") # <- and here
async def read_user(user_id: str): return {"user_id": user_id}
Thì nhớ để theo thứ tự /users/me trước rồi đến /users/{user_id} sau, ngược lại nếu /users/{user_id} ở trước thì sẽ nghĩ rằng "user_id" được nhận giá trị me.
Path in path
FastAPI hỗ trợ khai báo đường dẫn trong đường dẫn API nhờ vào việc based Starlette.
/files/{file_path}
file_path = /home/johndoe/myfile.txt
=> /files/home/johndoe/myfile.txt
from fastapi import FastAPI app = FastAPI() @app.get("/files/{file_path:path}")
async def read_file(file_path: str): return {"file_path": file_path}
Query Parameters
Nếu bạn truyền param dưới dạng key-value thì ở trong FastAPI có hỗ trợ với tên gọi "query" parameters.
from fastapi import FastAPI app = FastAPI() fake_items_db = [{"item_name": "Foo"}, {"item_name": "Bar"}, {"item_name": "Baz"}] # pair format: key-value @app.get("/items/")
async def read_item(skip: int = 0, limit: int = 10): return fake_items_db[skip : skip + limit] # trả về dữ liệu từ skip đến skip + limit
Kiểm tra ở link http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/?skip=0&limit=10:
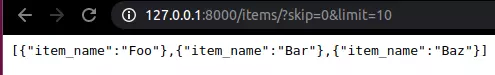
Nếu bạn để ý skip và limit có format string khi làm đường dẫn nhưng một khi truyền về hàm thì sẽ ngay lập tức được convert từ string về int.
Optional parameters
Ngoài ra FastAPI cung cấp một cách khai báo optional query parameters, mặc định là None.
from typing import Optional from fastapi import FastAPI app = FastAPI() @app.get("/items/{item_id}")
async def read_item(item_id: str, q: Optional[str] = None): ''' param item_id: format string param q: format string, default value: None, Optional: help you find error that happen ''' if q: return {"item_id": item_id, "q": q} return {"item_id": item_id}
Như bạn thấy ở trên param truyền ở đường dẫn là item_id, nhưng trong hàm có thêm param q. FastAPI chỉ sử dụng str để nhận định format của param còn Optional thì FastAPI không sử dụng, chỉ có tác dụng check lỗi nếu xảy ra.
Bạn có thể test bằng đường dẫn sau.
http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/1?q=1 # 1 là item_id và ?q=1 là giá trị của q
Query parameter type conversion
Thay đổi giá trị mặc định bằng cách truyền giá trị trên đường dẫn.
from fastapi import FastAPI app = FastAPI() @app.get("/items/{item_id}")
async def read_item(item_id: str, short: bool = False): # param short với định dạng boolean có giá trị mặc định là False item = {"item_id": item_id} if not short: item.update( {"description": "This is an amazing item that has a long description"} ) return item
Trong trường hợp này
http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/foo?short=1
or
http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/foo?short=True
Multiple path and query parameters
Với các đường dẫn lồng nhau, FastAPI biết param nào với param nào dựa trên tên param.
from fastapi import FastAPI app = FastAPI() @app.get("/users/{user_id}/items/{item_id}")
async def read_user_item(user_id: int, item_id: str): item = {"item_id": item_id, "owner_id": user_id} return item
Required query parameters
Đơn giản là bạn điền thiếu param trên đường dẫn sẽ báo lỗi
from fastapi import FastAPI app = FastAPI() @app.get("/items/{item_id}")
async def read_user_item(item_id: str, needy: str): item = {"item_id": item_id, "needy": needy} return item
Như hình dưới này, tôi chỉ truyền vào giá trị của item_id còn giá trị của needy thì không nên sinh ra lỗi.
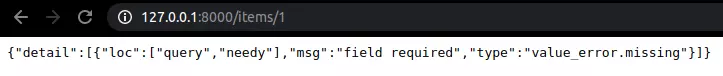
Request Body
- Request body: người dùng gửi request từ browser đến API.
- Response body: dựa trên request, APi trả về response cho người dùng.
Để khai báo format của request body, bạn cần sử dụng Pydantic models.
P/S: nhắc nhở khi send request cần sử dụng phương thức POST, nếu dùng phương thức GET thì bạn sẽ bị lộ thông tin trên URL => tính bảo mật không cao.
Pydantic Models
from typing import Optional
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel # import class BaseModel của thư viện pydantic class Item(BaseModel): # kế thừa từ class Basemodel và khai báo các biến name: str description: Optional[str] = None price: float tax: Optional[float] = None app = FastAPI() @app.post("/items/")
async def create_item(item: Item): # khai báo dưới dạng parameter return item
Ví dụ về 1 instance của class Item.
{ "name": "Foo", "description": "An optional description", "price": 45.2, "tax": 3.5
}
Do description và tax có giá trị None nên bạn có thể không cần thêm vào cũng được.
{ "name": "Foo", "price": 45.2
}
Dựa trên việc import Pydantic module, FastAPI hỗ trợ:
- Đọc request body dưới dạng Json.
- Chuyển đổi định dạng biến.
- Validate dữ liệu
- Khai báo format mặc định của request body, class Item trên là 1 ví dụ.
- Gen JSON Schema cho model của bạn
- Schema sẽ được gen thành UI của OpenAI doc.
Use model
Trong hàm create_item, bạn có thể tùy biến các biến của class Item, đơn giản như việc tính phí chịu thuế bằng cách tính tổng item.price và item.tax như bên dưới.
from typing import Optional from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel class Item(BaseModel): name: str description: Optional[str] = None price: float tax: Optional[float] = None app = FastAPI() @app.post("/items/")
async def create_item(item: Item): item_dict = item.dict() if item.tax: price_with_tax = item.price + item.tax item_dict.update({"price_with_tax": price_with_tax}) return item_dict
Request body + path parameters
FastAPI hỗ trợ khai báo tham số URL và request body cùng lúc, framework sẽ biết tham số nào truyền từ đường dẫn và tham số nào lấy từ request.
from typing import Optional from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel class Item(BaseModel): name: str description: Optional[str] = None price: float tax: Optional[float] = None app = FastAPI() @app.put("/items/{item_id}")
async def create_item(item_id: int, item: Item): return {"item_id": item_id, **item.dict()}
 P/S: tương tự như trên bạn có thể thêm tham số URL, tham số query và request body cùng lúc.
P/S: tương tự như trên bạn có thể thêm tham số URL, tham số query và request body cùng lúc.
Query Parameters and String Validations
Ở phần trước chúng ta đã biết khái niệm của query parameter rồi, lạ 1 loại param có cũng được không có cũng không sao. Param này có attribute là Optional, nhưng độ dài bị giới hạn không vượt quá 50 ký tự. Nên FastAPI cung cấp class Query.
from typing import Optional from fastapi import FastAPI, Query app = FastAPI() @app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: Optional[str] = Query(None, max_length=50)): results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]} if q: results.update({"q": q}) return results
Câu lệnh q: Optional[str] = Query(None) cũng tương tự q: Optional[str] = None nhưng Query cung cấp các param khác như max_lenght, min_lenght, regex, ... Bạn có thể tăng giới hạn ký tự thành 250 như thế này chỉ việc thay đổi giá trị tham số. (Mặc định của max_lenght là 50)
q: Optional[str] = Query(None, max_length=250)
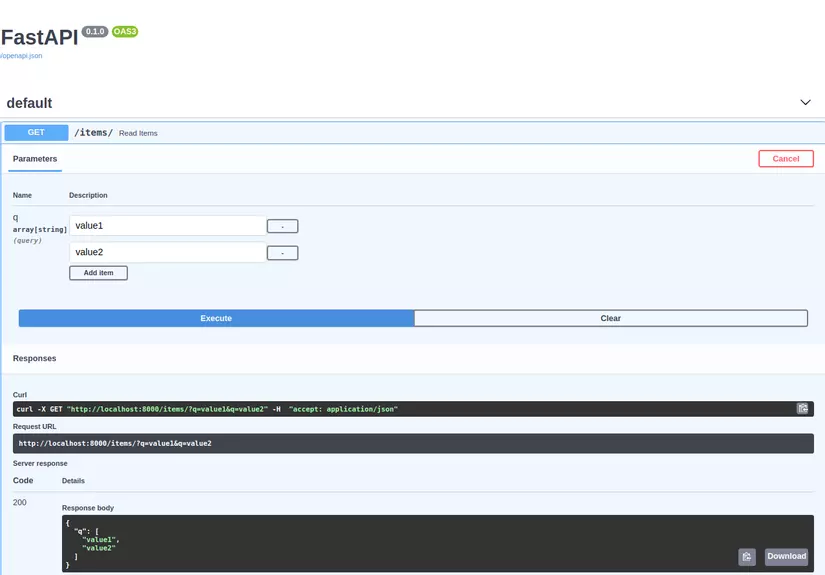
Query parameter list / multiple values
Ngoài định dạng string và integer, FastAPI còn hỗ trợ type List.
from typing import List, Optional from fastapi import FastAPI, Query app = FastAPI() @app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: Optional[List[str]] = Query(None)): query_items = {"q": q} return query_items
# q là 1 List có thể chứa nhiều giá trị.
http://localhost:8000/items/?q=foo&q=bar
Response body mà API trả về.
{ "q": [ "foo", "bar" ]
}
API cũng được cập nhật theo.
 P/S: bạn cũng có thể thay
P/S: bạn cũng có thể thay List[str] thành list như thế này.
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query app = FastAPI() @app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: list = Query([])): query_items = {"q": q} return query_items
Query còn 1 vài param nữa nhưng không quá quan trọng, bạn có thể vào doc của FastAPI để tìm hiểu chi tiết.
Các param mà Query cung cấp:
Metadata
alias: tên khác của paramtitle: metadata đặt tên paramdescription: metadata giới thiệu paramdeprecated: khi bạn chán param nào thì thêm vào để người dùng biết là bạn không còn sử dụng param đó nữa
Validation cho string:
min_lenghtmax_lenghtregex
Path Parameters and Numeric Validations
Query parameters có class Query để khai báo metadata và validations, Path parameters có class Pass với cơ chế tương tự.
Thêm title metadata cho path param item_id:
from typing import Optional from fastapi import FastAPI, Path, Query app = FastAPI() @app.get("/items/{item_id}")
async def read_items( item_id: int = Path(..., title="The ID of the item to get"), q: Optional[str] = Query(None, alias="item-query"),
): results = {"item_id": item_id} if q: results.update({"q": q}) return results
Number validations: greater than or equal
Chúng ta không chỉ có thể validate string mà còn validate được number.
Với param ge=1 của class Path, item_id bắt buộc phải là 1 số lớn hơn hoặc bằng 1
from fastapi import FastAPI, Path app = FastAPI() @app.get("/items/{item_id}")
async def read_items( *, item_id: int = Path(..., title="The ID of the item to get", ge=1), q: str
): results = {"item_id": item_id} if q: results.update({"q": q}) return results
Number validations: greater than and less than or equal
Tương tự với le=100, item_id bắt buộc phải là 1 số nhỏ hơn hoặc bằng 100.
item_id: int = Path(..., title="The ID of the item to get", gt=0, le=1000)
P/S: Number validations không chỉ hỗ trợ type integer mà còn hỗ trợ cho type float.
size: float = Query(..., gt=0, lt=10.5)
gt:ge:lt:le:
Body
Multiple Parameters
Đơn giản là FastAPI hỗ trợ tạo format cho request body, bạn có thể dùng không chỉ 1 mà là N Pydantic model như ví dụ dưới, tôi khai báo 2 class Item và User tương ứng 2 Pydantic model.
from typing import Optional from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel app = FastAPI() class Item(BaseModel): name: str description: Optional[str] = None price: float tax: Optional[float] = None class User(BaseModel): username: str full_name: Optional[str] = None @app.put("/items/{item_id}")
async def update_item(item_id: int, item: Item, user: User): results = {"item_id": item_id, "item": item, "user": user} return results
{ "item": { "name": "Foo", "description": "The pretender", "price": 42.0, "tax": 3.2 }, "user": { "username": "Hoang", "full_name": "Hoang Pham" }
}
Singular values in body
Bạn cũng có thể thêm define 1 body cho chỉ 1 giá trị mà không cần khai báo class, giả dụ ở đây tôi thêm 1 param là importance có type là int và cũng là 1 key nằm trong json body, nên khi post data thì bạn cũng phải khai báo giá trị cho importance.
async def update_item( item_id: int, item: Item, user: User, importance: int = Body(...)
):
{ "item": { "name": "Foo", "description": "The pretender", "price": 42.0, "tax": 3.2 }, "user": { "username": "Hoang", "full_name": "Hoang Pham" }, "importance": 5
}
Multiple body params and query
Nói đơn giản là kết hợp multiple body param với query param.
async def update_item( *, item_id: int, item: Item, user: User, importance: int = Body(..., gt=0), q: Optional[str] = None
): results = {"item_id": item_id, "item": item, "user": user, "importance": importance} if q: results.update({"q": q}) return results
Field
Để validate data hoặc thêm metadata trong 1 class giả dụ Item chẳng hạn, bạn cần import Field operation function từ module pydantic.
from typing import Optional from fastapi import Body, FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field app = FastAPI() class Item(BaseModel): name: str description: Optional[str] = Field( None, title="The description of the item", max_length=300 ) price: float = Field(..., gt=0, description="The price must be greater than zero") tax: Optional[float] = None @app.put("/items/{item_id}")
async def update_item(item_id: int, item: Item = Body(..., embed=True)): results = {"item_id": item_id, "item": item} return results
Như đoạn code ở trên param description có metadata là title, với length không vượt quá 300 từ, hay như param price không được nhỏ hơn 0 và có metadata là description.
Nested Models
Ngoài các kiểu int, float, str, bạn còn có thể thêm kiểu list hay set như dưới đây.
class Item(BaseModel): name: str description: Optional[str] = None price: float tax: Optional[float] = None tags: list = []
Với cách khai báo trên, khi post bạn truyền param là 1 list, nhưng với cách khai báo trên thì list này sẽ không xác định kiểu định dạng của từng phần tử trong list.
Không sao bởi Python có module List hỗ trợ bạn khai báo param là list xác định kiểu định dạng của từng phần tử.
from typing import List, Optional from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel app = FastAPI() class Item(BaseModel): name: str description: Optional[str] = None price: float tax: Optional[float] = None tags: List[str] = []
Tương tự với List, bạn có thể thêm Set.
from typing import Optional, Set class Item(BaseModel): name: str description: Optional[str] = None price: float tax: Optional[float] = None tags: Set[str] = set()
Ngoài ra các kiểu normal như str, int, float, ... FastAPI cũng hỗ trợ thêm các định dạng phức tạp và đa dạng hơn, giả sử định dạng HttpUrl kế thừa từ định dạng str. Để biết thêm chi tiết mời check link này (https://pydantic-docs.helpmanual.io/usage/types/).
- Tiếp sau đây tôi sẽ giới thiệu các bạn cách khai báo 1 model lồng trong 1 model khác như thế nào.
Giả sử tôi có 2 class Images và Item.
from typing import Optional, Set from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel app = FastAPI() class Image(BaseModel): url: str name: str class Item(BaseModel): name: str description: Optional[str] = None price: float tax: Optional[float] = None tags: Set[str] = []
Tôi muốn class Images nằm trong class Item như thế này.
{ "item": { "name": "Foo", "description": "The pretender", "price": 42.0, "tax": 3.2, "tags": ["rock", "metal", "bar"], "image": { "url": "http://example.com/baz.jpg", "name": "The Foo live" } }
}
Bạn chỉ cần thêm 1 dòng code vào class Item. Easy !
class Item(BaseModel): name: str description: Optional[str] = None price: float tax: Optional[float] = None tags: Set[str] = [] image: Optional[Image] = None
Bạn cũng có thể tùy biến định dạng của Pydantic models là list hoặc set chẳng hạn.
images: Optional[List[Image]] = None
Và đây là kết quả.
{ "name": "Foo", "description": "The pretender", "price": 42.0, "tax": 3.2, "tags": [ "rock", "metal", "bar" ], "images": [ { "url": "http://example.com/baz.jpg", "name": "The Foo live" }, { "url": "http://example.com/dave.jpg", "name": "The Baz" } ]
}
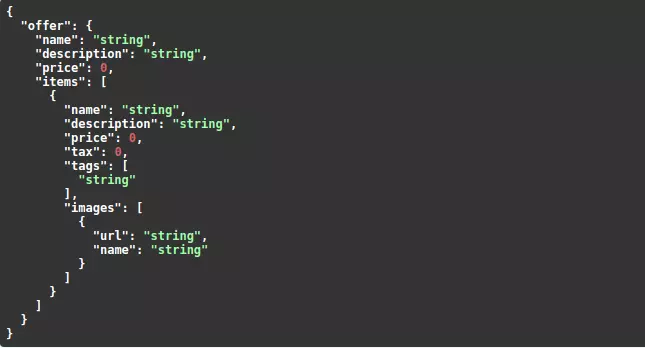
Trên lý thuyết bạn có thể lặp đi lặp lại các models lồng nhau như sau. Class Image nằm trong class Item, class Item thì lại nằm trong class Offer.
from typing import List, Optional, Set from fastapi import FastAPI, Body
from pydantic import BaseModel, HttpUrl app = FastAPI() class Image(BaseModel): url: HttpUrl name: str class Item(BaseModel): name: str description: Optional[str] = None price: float tax: Optional[float] = None tags: Set[str] = [] images: Optional[List[Image]] = None class Offer(BaseModel): name: str description: Optional[str] = None price: float items: List[Item] @app.post("/offers/")
async def create_offer(offer: Offer = Body(..., embed=True)): return offer
Kết luận
Do FastAPI là 1 framework API mới, có rất nhiều tính năng nên tôi chia ra thành nhiều phần (căn bản do không đủ kiên nhẫn để viết  ). Ở đây tôi sẽ chỉ liệt kê các tính năng quan trọng dùng nhiều trước rồi sau đó sẽ nâng cao lên trong các phần tiếp theo. Bạn cũng có thể xem thẳng trên doc của fastapi. Link tham khảo here:
). Ở đây tôi sẽ chỉ liệt kê các tính năng quan trọng dùng nhiều trước rồi sau đó sẽ nâng cao lên trong các phần tiếp theo. Bạn cũng có thể xem thẳng trên doc của fastapi. Link tham khảo here: