Giới thiệu
Chào mọi người đến với series practice về kubernetes. Ở bài này chúng ta sẽ tìm hiểu về cách triển khai một hệ thống database ở mode master-slave replication ở trên kubernetes.
Trước khi nói về cách trển khai hệ database, thì ta sẽ nói qua database master-slave replication là gì và tại sao ta lại cần nó?
Database Master-Slave Replication
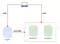
Đây là một hệ thống database bao gồm một master DB, và nhiều slave replication DB. Với master được sử dụng cho việc ghi dữ liệu, và các replication DB sẽ dùng cho việc đọc dữ liệu. Dữ liệu được ghi vào master DB sẽ được chuyển qua các replication DB để dữ liệu trên toàn hệ thống database của ta được đồng bộ với nhau.
Trong một ứng dụng, chúng ta chỉ thường xài một DB cho cả việc đọc và ghi, nếu ứng dụng chỉ là các ứng dụng web bình thường và có lượt truy cập không cao thì việc sử dụng một DB như vậy thì cũng đủ đáp ứng yêu cầu rồi. Nhưng đối với các ứng dụng mà có lượt truy cập cao, việc chỉ sử dụng một DB cho cả việc đọc và ghi, sẽ dẫn tới ứng dụng của chúng ta không thể đáp ứng được tất cả các lượt truy cập của user hoặc là ứng dụng ta sẽ có hiệu suất rất kém. Vì vậy nên hệ thống DB master-slave replication này sẽ giúp ta tăng hiệu suất xử lý của ứng dụng lên nhiều, bằng cách tách ra việc ghi dữ liệu sẽ được ghi vào một DB được gọi là master, và khi đọc dữ liệu thì ta sẽ đọc từ các DB read replicas => tăng hiệu suất và tốc độ xử lý của ứng dụng
Write k8s configuration file
Bây giờ ta sẽ tiến hành viết file cấu hình để triển khai hệ thống lên kubernetes, ở bài này mình sẽ sử dụng PostgreSQL.
Tạo master DB
Tạo một file tên là postgres-password-cm.yaml để chứa thông tin password của PostgreSQL DB.
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata: name: postgres-password
data: POSTGRES_USER: postgres POSTGRES_PASSWORD: postgres TIMESCALEDB_TELEMETRY: "off"
$ kubectl apply -f postgres-password-cm.yaml
configmap/postgres-password created
Vì để demo nên ta sẽ sử dụng ConfigMap cho nhanh, còn khi làm thực tế ta sẽ dùng Secret. Đầu tiên ta sẽ tạo master DB trước, tạo một file tên là postgres-master-sts.yaml:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet
metadata: name: postgres-master labels: component: postgres-master
spec: selector: matchLabels: component: postgres-master serviceName: postgres-master template: metadata: labels: component: postgres-master spec: containers: - name: postgres image: postgres:11 command: [ "sh", "-c", "docker-entrypoint.sh -c config_file=/var/config/postgresql.conf -c hba_file=/var/config/pg_hba.conf", ] ports: - containerPort: 5432 envFrom: - configMapRef: name: postgres-password volumeMounts: - mountPath: /var/lib/postgresql/data name: postgres-data-master - mountPath: /var/config name: postgres-master-configmap volumes: - name: postgres-master-configmap configMap: name: postgres-master-configmap volumeClaimTemplates: - metadata: name: postgres-data-master spec: accessModes: - ReadWriteOnce storageClassName: hostpath resources: requests: storage: 5Gi
Ở file config trên ta sử dụng image postgres:11, ở thuộc tính command ta sẽ truyền thêm vào câu lệnh để báo cho postgres biết là ta sẽ sử dụng custom config file cho nó, chứ không dùng config có sẵn của nó, hai file config ta chỉ định chỉ báo cho postgres biết nó đang là master DB. Để truyền hai file config trên vào DB được, ta sẽ sử dụng ConfigMap dạng volumeMounts, các bạn có thể đọc bài 8 của Kubernetes Series của mình để hiểu hơn về vấn đề này. ConfigMap chứa hai config đó có tên là postgres-master-configmap, giờ ta sẽ tạo nó.
Tạo một folder tên là config, mở nó ra và tạo thêm hai file tên là postgresql.conf và pg_hba.conf.
listen_addresses = '*'
max_connections = 100
shared_buffers = 128MB
dynamic_shared_memory_type = posix max_wal_size = 1GB
min_wal_size = 80MB
log_timezone = 'Etc/UTC'
datestyle = 'iso, mdy'
timezone = 'Etc/UTC'
lc_messages = 'en_US.utf8'
lc_monetary = 'en_US.utf8'
lc_numeric = 'en_US.utf8'
lc_time = 'en_US.utf8'
default_text_search_config = 'pg_catalog.english' #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# CUSTOMIZED OPTIONS
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------ # Add settings for extensions here
wal_level = replica
max_wal_senders = 2
max_replication_slots = 2
synchronous_commit = off
File này là mình copy từ trong docker ra, tất cả config từ chỗ comment # CUSTOMIZED OPTIONS trở lên là mặc định của file ở trong docker, ta thêm config cho master db từ chỗ # Add settings for extensions here trở xuống. Còn file pg_hba.conf thì sẽ như sau.
# TYPE DATABASE USER ADDRESS METHOD
local all all trust
# IPv4 local connections:
host all all 127.0.0.1/32 trust
# IPv6 local connections:
host all all ::1/128 trust
# Allow replication connections from localhost, by a user with the
# replication privilege.
local replication all trust
host replication all 127.0.0.1/32 trust
host replication all ::1/128 trust
host replication repuser 0.0.0.0/0 scram-sha-256
host all all all md5
Sau đó ta tạo ConfigMap.
$ kubectl create cm postgres-master-configmap --from-file=config
configmap/postgres-master-configmap created
Sau khi tạo được ConfigMap thì tiếp theo ta sẽ tạo StatefulSet ở trên.
$ kubectl apply -f postgres-master-sts.yaml
statefulset.apps/postgres-master created
Kiểm tra nó chạy được chưa.
$ kubectl get sts
NAME READY AGE
postgres-master 1/1 4s $ kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
postgres-master-0 1/1 Running 0 7s
Ok, vậy là ta đã tạo được master db, bây giờ ta sẽ truy cập vào nó và thực thi câu lệnh tạo user. Đây là user mà slave db sẽ sử dụng để connect được tới master.
$ kubectl exec -it postgres-master-0 -- bash
_@.com:/# su - postgres
_@.com:~$ psql
postgres=# SET password_encryption = 'scram-sha-256';
SET
postgres=# CREATE ROLE repuser WITH REPLICATION PASSWORD 'postgres' LOGIN;
CREATE ROLE
postgres=# SELECT * FROM pg_create_physical_replication_slot('replica_1_slot'); slot_name | lsn ----------------+----- replica_1_slot | (1 row)
Ok, cuối cùng là ta tạo Service resource để client có thể connect được tới master db này, tạo một file tên là postgres-master-svc.yaml.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata: name: postgres-master
spec: selector: component: postgres-master ports: - port: 5432
$ kubectl apply -f postgres-master-svc.yaml
service/postgres-master created
Chuẩn bị dữ liệu cho slave DB
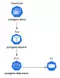
Thì để tạo được slave DB, PostgreSQL yêu cầu ta phải sync dữ liệu từ master DB ra, sau đó khởi tạo các slave DB với data là từ data được sync này. Để làm được việc này trong kubernetes, đầu tiên ta sẽ tạo một PVC, và chạy một Job để sync data từ master DB vào PVC này, sau đó ta sẽ tạo slave DB mà dữ liệu sẽ được mount từ PVC này ra. Minh họa như sau.

Tạo một file tên là pvc-slave.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata: name: postgres-data-slave
spec: accessModes: - ReadWriteOnce storageClassName: hostpath resources: requests: storage: 5Gi
$ kubectl apply -f pvc-slave.yaml
persistentvolumeclaim/postgres-data-slave created
Ta tạo Job resource để chạy sync dữ liệu từ master DB vào PVC ở trên, tạo một file tên là sync-master-data.yaml
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata: name: sync-master-data
spec: template: spec: restartPolicy: OnFailure containers: - name: sync-master-data image: postgres:11 command: [ "sh", "-c", 'PGPASSWORD="postgres" pg_basebackup -h postgres-master -D /var/lib/slave-postgresql/data -U repuser -vP', ] volumeMounts: - mountPath: /var/lib/slave-postgresql/data name: postgres-data volumes: - name: postgres-data persistentVolumeClaim: claimName: postgres-data-slave
$ kubectl apply -f sync-master-data.yaml
job.batch/sync-master-data created
Log job ra.
$ kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
postgres-master-0 1/1 Running 0 89m
sync-master-data-59jhb 0/1 Completed 0 3s $ kubectl logs sync-master-data-59jhb
pg_basebackup: initiating base backup, waiting for checkpoint to complete
pg_basebackup: checkpoint completed
pg_basebackup: write-ahead log start point: 0/2000028 on timeline 1
pg_basebackup: starting background WAL receiver
pg_basebackup: created temporary replication slot "pg_basebackup_143" 0/23770 kB (0%), 0/1 tablespace (...ave-postgresql/data/backup_label)
23779/23779 kB (100%), 0/1 tablespace (...ostgresql/data/global/pg_control)
23779/23779 kB (100%), 1/1 tablespace pg_basebackup: write-ahead log end point: 0/20000F8
pg_basebackup: waiting for background process to finish streaming ...
pg_basebackup: base backup completed
Ta sẽ thấy job của ta đã chạy sync data vào PVC thành công.
Tạo slave DB
Giờ ta sẽ tạo slave DB. Đầu tiên ta sẽ tạo ConfigMap để chứa config mà báo cho DB biết nó sẽ là slave DB, tạo một folder tên là slave-config, tạo hai file là postgresql.conf với recovery.conf
listen_addresses = '*'
max_connections = 100
shared_buffers = 128MB
dynamic_shared_memory_type = posix max_wal_size = 1GB
min_wal_size = 80MB
log_timezone = 'Etc/UTC'
datestyle = 'iso, mdy'
timezone = 'Etc/UTC'
lc_messages = 'en_US.utf8'
lc_monetary = 'en_US.utf8'
lc_numeric = 'en_US.utf8'
lc_time = 'en_US.utf8'
default_text_search_config = 'pg_catalog.english' #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# CUSTOMIZED OPTIONS
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------ # Add settings for extensions here
hot_standby = on
wal_level = replica
max_wal_senders = 2
max_replication_slots = 2
synchronous_commit = off
standby_mode = on
primary_conninfo = 'host=postgres-master port=5432 user=repuser password=postgres application_name=r1'
primary_slot_name = 'replica_1_slot'
trigger_file = '/var/lib/postgresql/data/change_to_master'
Tạo ConfigMap.
$ kubectl create cm postgres-slave-configmap --from-file=slave-config
configmap\postgres-slave-configmap
Tiếp theo, ta sẽ tạo StatefulSet mà mount vào PVC ta tạo ở trên, nó sẽ có thông tin dữ liệu được sync từ master db.
Tạo một file tên là postgres-slave-sts.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet
metadata: name: postgres-slave labels: component: postgres-slave
spec: selector: matchLabels: component: postgres-slave serviceName: postgres-slave template: metadata: labels: component: postgres-slave spec: initContainers: - name: busybox image: busybox command: - sh - -c - "cp /var/config/postgresql.conf /var/lib/postgresql/data/postgresql.conf && cp /var/config/recovery.conf /var/lib/postgresql/data/recovery.conf" volumeMounts: - mountPath: /var/lib/postgresql/data name: postgres-data - mountPath: /var/config/postgresql.conf subPath: postgresql.conf name: postgres-slave-configmap - mountPath: /var/config/recovery.conf subPath: recovery.conf name: postgres-slave-configmap containers: - name: postgres image: postgres:11 ports: - containerPort: 5432 envFrom: - configMapRef: name: postgres-password volumeMounts: - mountPath: /var/lib/postgresql/data name: postgres-data volumes: - name: postgres-slave-configmap configMap: name: postgres-slave-configmap - name: postgres-data persistentVolumeClaim: claimName: postgres-data-slave
Ở file config trên, vì mình không kiếm được câu config để postgres chỉ định custom recovery.conf config file, nên mình dùng initContainers để khởi tạo config, bằng cách mount ConfigMap vào initContainers, sau đó sẽ dùng thuộc tính command để thực hiện câu lệnh copy file config từ initContainers sang PVC, và main container postgres sẽ mount vào PVC đó, nó sẽ có được hai file copy ở trên. Ok, giờ ta tạo slave DB.
$ kubectl apply -f postgres-slave-sts.yaml
statefulset.apps/postgres-slave created
Khi bạn log db ra, bạn sẽ thấy nó có hiển thị dòng là db chỉ dùng để đọc, không thể ghi được.
$ kubectl logs postgres-slave-0
PostgreSQL Database directory appears to contain a database; Skipping initialization ...
2021-12-10 08:57:29.790 UTC [1] LOG: database system is ready to accept read only connections
Vậy là slave DB của ta đã được tạo thành công, bước cuối là ta kiểm tra xem khi ta insert dữ liệu vào master DB thì slave DB của ta có dữ liệu giống y change như master hay không. Truy cập vào master DB.
$ kubectl exec -it postgres-master-0 -- psql -h localhost -U postgres -d postgres
psql (11.12 (Debian 11.12-1.pgdg90+1))
Type "help" for help. postgres=# CREATE TABLE test (id int not null, val text not null);
CREATE TABLE
postgres=# INSERT INTO test VALUES (1, 'foo');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# INSERT INTO test VALUES (2, 'bar');
INSERT 0 1
Sau khi insert dữ liệu xong thì ta truy cập vào slave DB.
$ kubectl exec -it postgres-slave-0 -- psql -h localhost -U postgres -d postgres
psql (11.12 (Debian 11.12-1.pgdg90+1))
Type "help" for help. postgres=# SELECT * FROM test; id | val ----+----- 1 | foo 2 | bar
(2 rows)
Ta thực hiện câu lệnh select và thấy hai dữ liệu khi nãy ta đã insert vào master. Ok, ta đã triển khai được mô hình database master-slave replication trên kubernetes thành công ?. Thì đây là để demo, trong production thì ta có thể triển khai nhanh hơn bằng cách sử dụng công cụ có sẵn của kubernetes, là Helm, nó sẽ giúp ta triển khai mô hình này một cách nhanh chóng chỉ bằng 1-2 câu CLI, và ta cũng chả cần phải viết file config.
Tạo bằng Helm
Helm là một package manager cho kubernetes. Đầu tiên muốn xài thì bạn cần cài trước, các bạn xem cách cài ở đây https://helm.sh/docs/intro/install/. Sau khi cài xong thì ta chạy những câu lệnh sau đây để triển khai database.
$ helm repo add bitnami https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami
"bitnami" has been added to your repositories $ helm install postgresql bitnami/postgresql-ha --set postgresqlPassword=postgres --set replication.password=postgres
Sau khi tạo xong bạn get pod ra xem thì sẽ thấy có 3 pod postgresql được deploy.
$ kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
postgresql-postgresql-ha-pgpool-65fbd4fb4b-vzsjn 0/1 Running 0 114s
postgresql-postgresql-ha-postgresql-0 1/1 Running 0 114s
postgresql-postgresql-ha-postgresql-1 1/1 Running 0 114s
PostgreSQL HA Helm chart sẽ triển khai một cluster với 3 pod, một cho pgpool, một cho master và một cho slave. Sử dụng Helm ta có thể triển khai mọi thứ rất nhanh, chỉ cần hai câu CLI.
Kết luận
Vậy là ta đã tìm hiểu xong cách triển khai mô hình database dạng master-slave replication trên kubernetes. Nếu các bạn có thắc mắc hoặc chưa hiểu rõ chỗ nào, các bạn có thể hỏi ở phần comment.