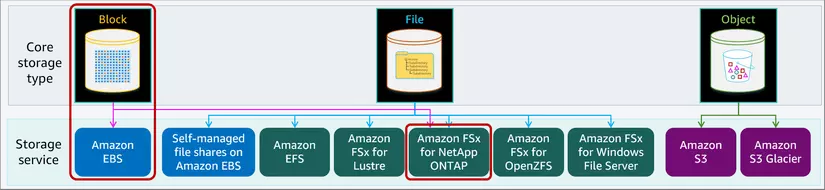
Block Storage: Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS)
The AWS block storage portfolio consists of two types of block storage services: Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instance storage and Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS). Amazon EBS also includes an integrated snapshot service. Amazon EBS is the primary block storage service.
Amazon FSx for NetApp ONTAP also offers block storage services over an iSCSI access protocol. These block services use NetApp's application programming interface (API) calls and management interface. For customer's seeking an integrated NetApp approach, block storage is available as part of the Amazon FSx service.
1. Amazon EC2 instance store
An instance store provides temporary (ephemeral) block-level storage for your instance. This storage is located on disks that are physically attached to the host computer where the compute instance is. Instance stores resemble Amazon EBS storage in initial configuration options. However, their architecture most closely resembles direct attached disk drives. An instance store provides submillisecond latencies between the EC2 instance and the storage.
Only specific Amazon EC2 instance types support instance stores. The available storage type is directly associated to the EC2 instance type. An instance store consists of one or more instance store volumes exposed as block devices. The size of an instance store and the number of devices available vary by instance type.
Instance store is ideal for the following use cases:
- Temporary storage of information that changes frequently, such as buffers, caches, scratch data, and other temporary content
- Data that is replicated across a fleet of instances, such as a load-balanced pool of web servers
Instances stores are not recommended for most block storage workloads.
As ephemeral storage, instance stores are not replicated or spread across multiple devices to improve durability and availability. An instance store is nonpersistent and is terminated when the associated EC2 instance is terminated.
Instance store lifetime
The data in an instance store persists only during the lifetime of its associated EC2 instance. If an instance reboots (intentionally or unintentionally), data in the instance store persists. However, data in the instance store is lost under any of the following circumstances:
- The underlying disk drive fails
- The instance stops
- The instance hibernates
- The instance terminates
Therefore, do not rely on an instance store for valuable, long-term data. Instead, use more durable data storage, such as Amazon EBS, for your block storage requirements.
2. Amazon EBS overview
Amazon EBS is an easy-to-use, high performance, block storage service. It is designed for use with Amazon EC2 compute instances for both throughput and transaction-intensive workloads at any scale.
AWS recommends Amazon EBS for data that must be quickly accessible and requires long-term persistence. EBS volumes are well suited for use as the primary storage for file systems, databases, or any applications that require fine granular updates and access to raw, unformatted, block-level storage. Amazon EBS is well suited to both database-style applications that rely on random reads and writes and to throughput-intensive applications that perform long, sequential reads and writes.
EBS volumes behave like raw, unformatted block devices. You can mount these block devices as EBS volumes on your EC2 instances. EBS volumes that are attached to an EC2 instance are exposed as raw block storage volumes that persist independently from the life of the instance. You can create a file system on top of these volumes or use them in any way you would use a block device (such as a hard drive). You can dynamically change the configuration of a volume attached to an EC2 instance, unlike traditional disk drives that come in fixed sizes.
You can choose from different EBS volume types to balance optimal price and performance. You can achieve single-digit millisecond latency for high-performance database workloads, such as SAP HANA, or gigabyte-per-second throughput for large, sequential workloads such as Apache Hadoop. You can change EBS volume types, tune performance, or increase volume size without disrupting your critical applications. Amazon EBS provides you cost-effective block storage when you need it.
Designed for mission-critical systems, EBS volumes are replicated within an AWS Availability Zone and can scale to store petabytes of data. Also, you can use EBS snapshots with automated lifecycle policies to back up your volumes in Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3). You can do this while ensuring geographic protection of your data and business continuity.
With Amazon EBS, you pay only for the storage and resources that you provision.
3. Amazon EBS features
Single Availability Zone
You create an EBS volume in a specific Availability Zone, and then attach it to an EC2 instance in that same Availability Zone. The proximity of your Amazon EBS volume to your Amazon EC2 instance provides low latency and high-performance block storage for your workload.
To make a volume available outside of the Availability Zone, you can create a snapshot and restore that snapshot to a new volume anywhere in the same AWS Region. You can also copy snapshots to other AWS Regions and then restore them to new volumes there. Snapshots make it easier to use multiple AWS Regions for geographical expansion, data center migration, and disaster recovery.
Persistent
Amazon EBS volumes are durable and persistent by default. Your EBS volume survives even if your EC2 instance is terminated. Your data is preserved for your future use and persists until you decide to delete it. Root EBS volumes created with an EC2 instance are terminated with the instance by default. However, you can modify the volume to be persistent.
EBS volumes are managed independently from the Amazon EC2 instances to which they are attached. You can detach an existing EBS volume from an EC2 instance and reattach it to a different EC2 instance. This provides you the ability to change EC2 instance types to meet your performance requirements and optimize your Amazon EC2 costs.
Volume types
Amazon EBS provides multiple volume types that you can use to optimize storage performance and cost for a broad range of applications. These volume types are divided into two major categories: SSD-backed storage for transactional workloads, such as databases, virtual desktops, and boot volumes, and HDD-backed storage for throughput-intensive workloads, such as MapReduce and log processing.
- SSD-based volumes include two levels to meet your application requirements: General Purpose SSD volumes and Provisioned IOPS SSD volumes.
- General Purpose SSD volumes (gp3 and gp2) balance price and performance for transactional applications, including virtual desktops, test and development environments, and interactive gaming applications.
- Provisioned IOPS SSD volumes are the highest performance EBS volumes (io2 and io1) for your most demanding transactional applications, including SAP HANA, Microsoft SQL Server, and IBM DB2.
- HDD-based volumes include Throughput Optimized HDD (st1) for frequently accessed, throughput-intensive workloads and the lowest cost Cold HDD (sc1) for less frequently accessed data. You can choose the volume type that best meets your application and use case requirements. You can change from one volume type to another.
Elastic volumes
Using the Elastic Volumes feature, you can adapt your volumes as the needs of your applications change. Use this feature to increase capacity, tune performance, and change the type of any new or existing current generation volume dynamically, with no downtime or performance impact. You can easily right-size your deployment and adapt to performance changes.
The Elastic Volumes feature makes it easier to adapt your resources to changing application demands. You can make modifications in the future as your business needs change.
High avaliability and high durability
EBS volumes are designed to be highly available, reliable, and durable at no additional charge to you. EBS volume data is replicated across multiple servers in an Availability Zone to prevent the loss of data from the failure of any single component.
Amazon EBS volumes are designed to provide 99.8–99.9 percent durability with an annual failure rate (AFR) of 0.1–0.2 percent. Amazon EBS also supports a snapshot feature, which is a good way to take point-in-time backups of your data.
Amazon EBS offers a higher durability io2 volume that is designed to provide 99.999 percent durability with an AFR of 0.001 percent. In this case, failure refers to a complete or partial loss of the volume. This makes io2 ideal for business-critical applications, such as SAP HANA, Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server, and IBM DB2, that will benefit from higher uptime.
Data encryption
You can create your EBS volumes as encrypted volumes to meet a wide range of data-at-rest encryption requirements for regulated/audited data and applications. When you create an encrypted EBS volume and attach it to a supported instance type, data stored at rest on the volume, disk I/O, and snapshots that were created from the volume are all encrypted. The encryption occurs on the servers that host EC2 instances, providing encryption of data in transit from EC2 instances to Amazon EBS storage.
Native snapshot support
You can create point-in-time snapshots of EBS volumes, which are persisted to Amazon S3. Snapshots protect data for long-term durability. You can use snapshots to restore your data to new volumes, expand the size of a volume, or move volumes across Availability Zones. The same snapshot can be used to instantiate as many volumes as you want. You can copy these snapshots across AWS Regions. You pay for only the storage capacity consumed for your snapshot data.
Snapshots let you geographically protect your data and achieve business continuity. You can use Amazon Data Lifecycle Manager (Amazon DLM) to automate snapshot management without any additional overhead or cost.
AWS Backup support
AWS Backup supports backing up your EBS volumes. With AWS Backup, you can centralize and automate data protection across multiple Amazon EBS volumes. AWS Backup offers a cost-effective, fully managed, policy-based service that further simplifies data protection at scale.
AWS Backup also helps you support your regulatory compliance obligations and meet your business continuity goals.
Performance monitoring
Performance metrics, such as bandwidth, throughput, latency, and average queue length, are available through the AWS Management Console. Amazon CloudWatch provides these metrics so that you can monitor the performance of your volumes. You can make sure that you are providing enough performance for your applications and paying only for resources you need.
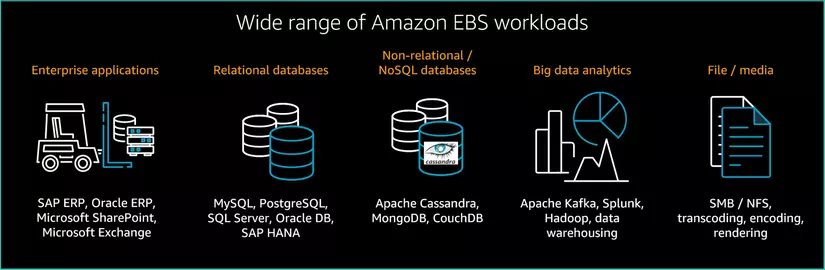
Amazon EBS use cases
The functionality and available performance options make Amazon EBS a good storage option for many workloads and use cases. In this section, you will learn about the most common use cases for Amazon EBS storage, including enterprise applications, relational databases, nonrelational (NoSQL) databases, big data analytics, and file systems and media workflows.
Lift and shift on-premises applications using Amazon EBS
Most organizations have on-premises applications burdened with high capital expenses, complex management, scalability challenges, and hardware that needs to be replaced every 3–5 years.
Maintaining existing on-premises infrastructure results in increased operational burden. This maintenance drains IT budgets for organizations that are already budget and resource strapped. With these on-premises challenges, IT organizations want to move to the cloud and away from the traditional, costly lifecycle of buying, managing, and replacing on-premises hardware, software, services, and networking.
Most cloud migrations happen in phases to minimize risk and shorten time to production. The most common approach is to lift and shift an application and its data with as few changes as possible to similar services running in the cloud. This provides the fastest time to production. After the application is on AWS, you can modernize and re-architect application elements to take advantage of the cloud services and optimizations that provide the most significant benefits.
Pricing
With Amazon EBS, you pay only for what you use. Pricing for EBS volumes is based on the volume type, provisioned volume size, and the provisioned IOPS and throughput performance. EBS volume pricing varies based on the Availability Zone where it resides. The pricing for Amazon EBS snapshots is based on the actual amount of storage space that you use.